Natalia Rodon1, Yessica No Garbarino1, Olga Diaz1 and Xavier Puig1,2,3.
1BIOPAT. Biopatologia Molecular SL. Grup Assistència. Barcelona, Spain. 2HISTOPAT SL. Barcelona, Spain. 3SCIAS-Hospital de Barcelona, Grup Assistència. Barcelona, Spain.
BACKGROUND
Mismatch repair (MMR) deficiency and microsatellite instability (MSI) are approved predictive biomarkers of PD1/PD-L1 therapy in colorectal cancer (CRC) patients. Tumor Mutational Burden (TMB) quantifies the number of somatic mutations in tumoral DNA and is reported as number of mutations per DNA Megabase (mut/Mb). TMB is being investigated as a novel predictive biomarker for immune checkpoint inhibitors. In this study we explore the feasibility and potential utility of calculating TMB with a next-generation sequencing (NGS) based panel and its correlation with MMR and MSI.
DESIGN
We designed a nested case-control study in our cohort of CRC patients with complete morpho-molecular characterization since 2009. All patients had previous MSI assessment with a 5 microsatellites panel kit (MSI Analysis System, Promega) and immunohistochemical analysis of MMR proteins (MLH1, MSH2, MSH6 and PMS2). Cases (high-MSI) were defined as CRC patients with MSI. Controls (MSS, 1:1) were selected among CRC patients without high-MSI. Genomic DNA was extracted from paired FFPE normal and malignant tissue sections (RecoverAll Kit for FFPE, ThermoFisher). TMB was assessed with a targeted NGS assay detecting somatic mutations and Indels from 409 genes, spanning 1.7 Mb of genomic space (Oncomine TMB. Thermofisher). High-TMB was defined as ≥ 10 mut/Mb. Analysis was performed using SSPS v20.
RESULTS
Sixty CRC patients were included: 30 high-MSI and 30 MSS without differences regarding age or gender (68% females, median age 68 years). The concordance rate between MSI status and MMR expression was 97.7%. All but one TMB studies were informative. Median TMB was higher in the high-MSI group compared to the MSS group [28.1 (15.2-50.2) vs 5.3 (1.7-18.5) Mut/Mb respectively, p=0.000]. A TMB threshold ≥ 10 mut/Mb was associated with a high-MSI status in 98.3%. One (3.4%) MSS tumor with no MMR deficiency showed an unexpected high-TMB (18.48mut/Mb) (Figure 1).
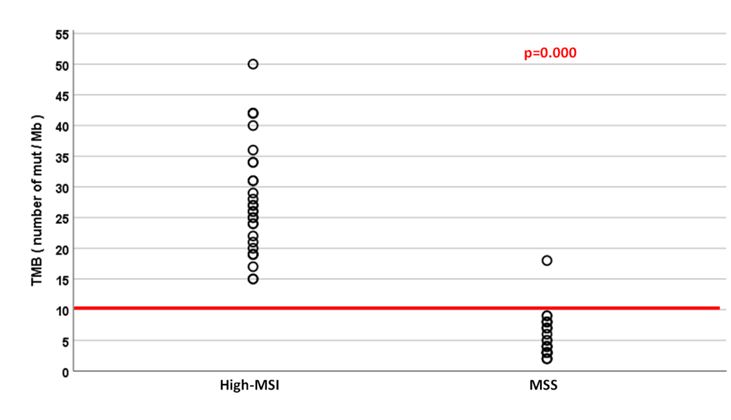
Figure 1. TMB (Number of mutations/Mb) according to MSI status.
CONCLUSION
The concordance rate between MSI status and TMB in CRC is excellent. A TMB threshold ≥ 10mut/Mb accurately identifies CRC patients with high-MSI. TMB is able to identify 1 in 30 patients suitable to respond to immunotherapy not previously detected by MSI or MMR studies.
Abstract exhibited at the:
109th ANNUAL MEETING OF THE UNITED STATES AND CANADIAN ACADEMY OF PATHOLOGY
LOS ANGELES, MARCH 2020
